Exchange-traded funds have become one of the fastest on-ramps for mainstream capital to reach digital assets. In fewer than eighteen months, spot Bitcoin ETFs, publicly traded vehicles that hold the underlying coins in cold custody, have attracted more than US $52 billion in assets, eclipsing early forecasts for the entire first five years of inflows.
Crypto ETF explained headlines now dominate financial media as regulators widen the doorway to ether and multi-asset products. Understanding how these funds are structured, created, and traded is essential for anyone tracking the next phase of institutional crypto adoption.
From Gold to Bitcoin: A Short History
The earliest commodity ETFs, such as SPDR Gold Shares in 2004, demonstrated that wrapping a hard asset in an exchange-listed wrapper could unlock vast pools of demand. The crypto industry followed that blueprint for years, winning U.S. approval for futures-based Bitcoin ETFs in 2021 before the watershed January 2024 green-light for spot vehicles.
By July 2025, BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) alone was generating an estimated US $187 million in annual fees, rivaling its flagship S&P 500 fund despite a fraction of the assets. Crypto ETF explained stories increasingly cite this fee momentum as proof that digital assets have secured a permanent seat at the Wall Street table.
Mechanics: Creation, Redemption, and Custody
At their core, crypto ETFs mirror traditional commodity or equity ETFs. Authorized participants (large broker-dealers) deliver bitcoin, ether, or a pre-defined basket of coins to the fund administrator in exchange for newly issued ETF shares, a process called “creation.” Shares can also be redeemed for the underlying assets, helping the ETF’s market price stay close to net asset value.
Dedicated custodians such as Coinbase Trust or BitGo hold the private keys in institutional-grade cold storage, and daily on-chain attestations verify balances for regulators and investors. With Crypto ETF explained in plain language, this creation-redemption loop is what keeps spreads tight and gives arbitrageurs a profit motive to police pricing.
Types of Crypto ETFs
| Structure | Underlying Exposure | U.S. Launch Year | Typical Expense Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Futures-Based | CME bitcoin or ether futures contracts | 2021 | 0.94 %–1.25 % |
| Spot Single-Asset | Physical bitcoin or ether held in cold storage | 2024 (BTC), 2025 (ETH) | 0.19 %–0.25 % |
| Spot Basket | Market-cap-weighted basket (BTC, ETH, SOL, XRP, ADA, etc.) | 2025 | 0.39 %–0.59 % |
Crypto ETF explained comparisons often highlight the cost advantage of spot funds: fewer roll costs and tighter tracking error versus futures products.
Current Market Landscape
Bitcoin ETFs: Eleven issuers compete for flows, led by IBIT and Fidelity’s FBTC, with cumulative net inflows near US $49 billion through July 2 2025.
Ether ETFs: The SEC approved spot ether products in April 2025 and even cleared listed options on BlackRock’s ETHA, though flows remain muted at roughly 25 % of Bitcoin’s pace as investors weigh the lack of staking yield.
Multi-Asset Funds: Grayscale’s Digital Large Cap Fund (GDLC) received conversion approval on July 1 2025, offering five-coin exposure in a single ticker, another step toward index-style crypto investing.
With each milestone, analysts publish a fresh Crypto ETF explained primer for wealth managers who can now allocate to digital assets without setting up private-key workflows.
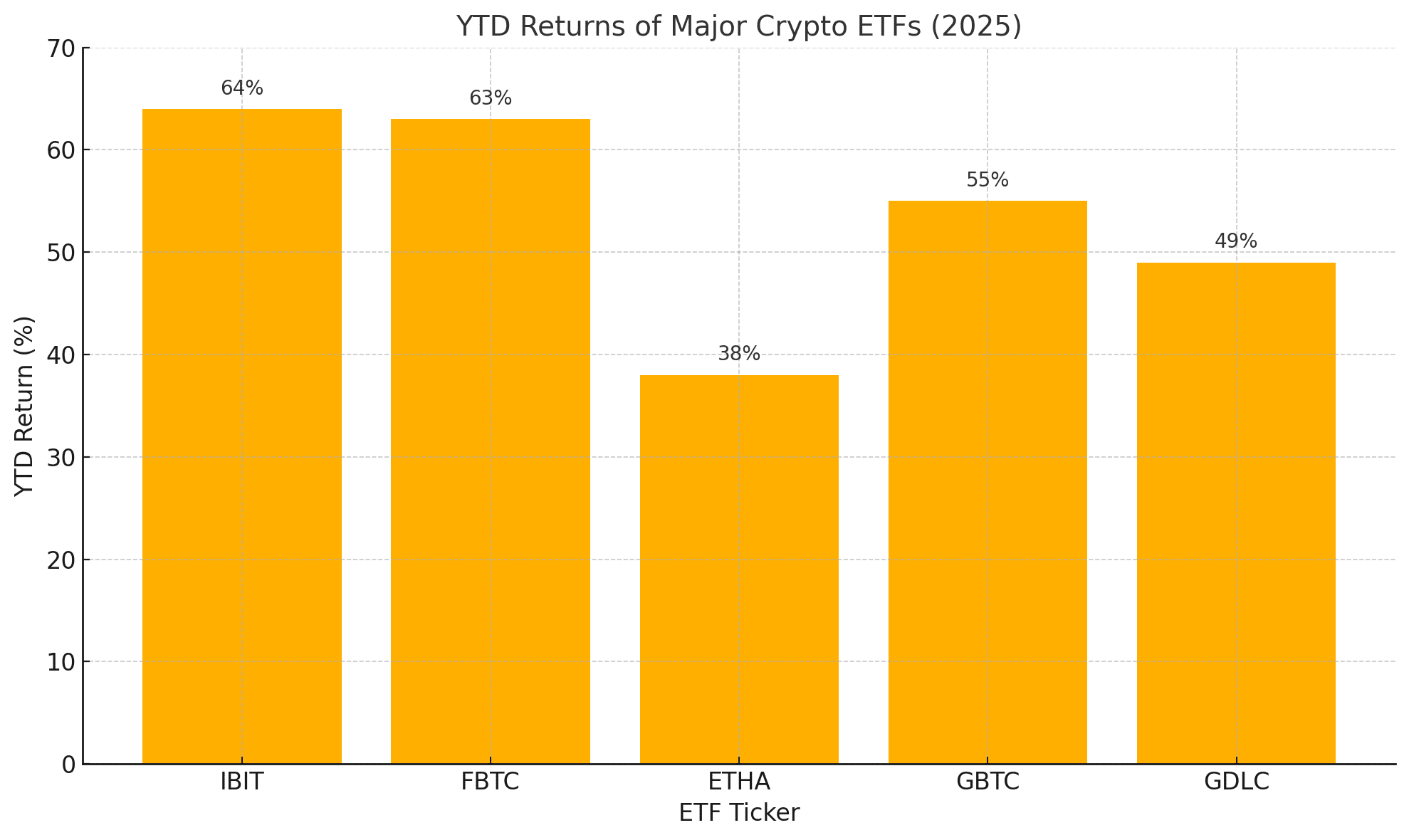
Performance (YTD 2025)
| Ticker | Asset Class | AUM (US $) | YTD Return | Expense Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBIT | Spot Bitcoin | 52 B | +64 % | 0.25 % |
| FBTC | Spot Bitcoin | 15 B | +63 % | 0.25 % |
| ETHA | Spot Ether | 7 B | +38 % | 0.24 % |
| GBTC | Converted Spot BTC | 22 B | +55 % | 1.50 % |
| GDLC | Spot Basket | 3 B | +49 %* | 0.59 % |
Benefits and Risks
Benefits
Regulated Access: Exchange listing places crypto under the 1940 Act and SEC disclosure regimes.
Tax Simplicity: 1099 forms replace the complexity of tracking on-chain cost basis.
Liquidity and Price Discovery: Daily volume across venues exceeds that of many blue-chip equities.
Risks
Premium/Discount Volatility: Although creation redemption narrows gaps, sharp overnight moves can widen them.
Custody Vulnerabilities: Cold storage mitigates hacks, yet operational failures remain a non-zero risk.
Regulatory Shifts: Congress or the SEC could alter capital requirements, stakeholder prohibitions, or reserve audits—core variables frequently cited in Crypto ETF explained risk sections.
Latest Developments Worth Watching
Options Liquidity: Approval of ether-ETF options could deepen hedging markets and attract professional traders.
Fee Wars: VanEck slashed its Bitcoin ETF fee to 0.19 %, pressuring rivals and improving investor net returns.
Global Expansion: The U.K. Financial Conduct Authority is reviewing its first batch of spot products, while Hong Kong doubled the quota on in-kind redemptions.
Every headline spawns another Crypto ETF explained explainer across financial blogs, solidifying the term’s position atop Google’s trending searches.
Expert Commentary
Bloomberg ETF analyst James Seyffart argues that Bitcoin funds already “behave like seasoned commodity ETFs,” citing low tracking error and narrowing bid-ask spreads, while Morningstar flags continued outperformance versus gold ETPs on risk-adjusted bases. A Reuters survey of family offices shows 31 % intend to use spot crypto ETFs as their primary digital-asset exposure by year-end 2025, up from 4 % before approval. Crypto ETF explained case studies increasingly feature these adoption metrics to highlight the velocity of institutional uptake.
Conclusion
Spot, futures, and basket-style offerings have transformed cryptocurrency from a niche asset class into a line item on traditional brokerage statements. The creation-redemption mechanism, rigorous custody, and SEC disclosure rules mean the ETF wrapper now delivers crypto exposure with the transparency and operational familiarity investors expect from equities or commodities.
As competitors race to cut fees and add staking-enabled coins once policy permits, Crypto ETF explained articles will remain essential reading for asset allocators weighing both the promise and the pitfalls of this rapidly evolving market.
FAQs
How does a spot crypto ETF maintain price parity with the underlying asset?
Authorized participants create or redeem shares in exchange for the underlying coins, arbitraging away premiums or discounts.
Why are ether ETF flows smaller than bitcoin’s?
The absence of staking yield and a smaller market cap dampen relative demand.
Can investors redeem ETF shares for actual crypto?
In-kind redemptions are limited to authorized participants; most retail holders receive cash proceeds from secondary-market sales.
Do crypto ETFs eliminate all custody risk?
They outsource custody to institutional providers, reducing but not eliminating operational and regulatory risk.
Glossary
Authorized Participant (AP): Broker-dealer permitted to create or redeem ETF shares.
Cold Storage: Offline wallet method used to secure ETF reserves from hacks.
Tracking Error: The divergence between an ETF’s market price and its net asset value.
Premium/Discount: The percentage by which an ETF’s share price trades above or below its NAV.
Expense Ratio: Annual fee, expressed as a percentage of average net assets, charged by the fund.