In the vast realm of digital currencies, where transactions are intangible and assets exist solely in cyberspace, the concept of a physical Bitcoin might seem paradoxical. Yet, in 2011, a visionary named Mike Caldwell bridged this digital-physical divide with the creation of Casascius coins, offering enthusiasts a tangible representation of the pioneering cryptocurrency.
The Genesis of Physical Bitcoin
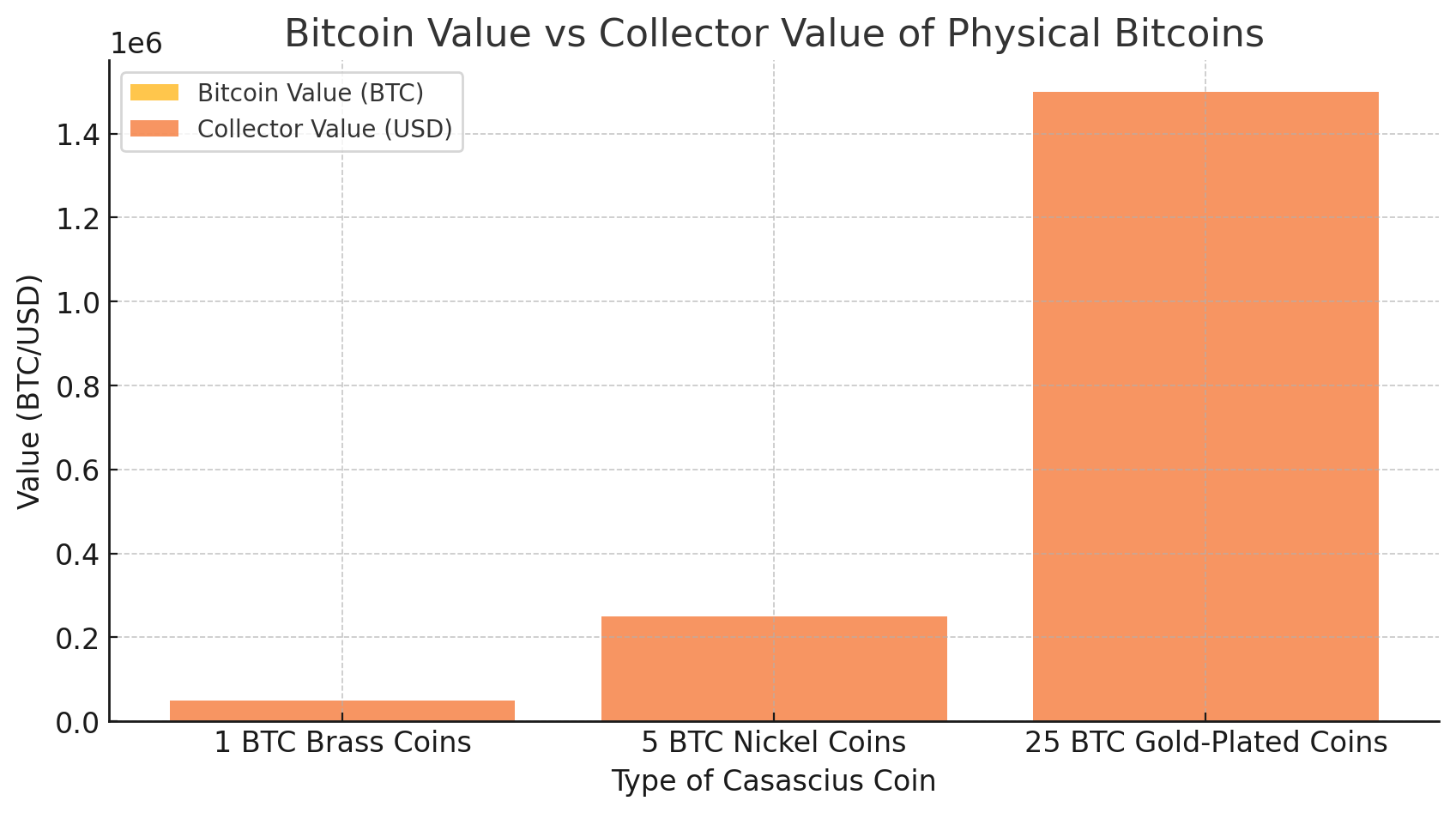
Mike Caldwell, a software engineer from Utah, introduced the world to Casascius coins in 2011. These physical embodiments of Bitcoin were meticulously crafted metal tokens, each embedded with a private key corresponding to a specific amount of digital Bitcoin. By concealing the private key beneath a tamper-evident holographic seal, Caldwell ensured both the digital asset’s security and the physical coin’s integrity. This innovation allowed individuals to hold, exchange, and even gift Bitcoins in a form that was both familiar and tangible. Below is the chart, showing about Physical Bitcoin:
Design and Denominations
Casascius coins were produced in various denominations, catering to a wide range of users:
1 BTC Brass Coins: These were the most common, featuring a brass composition with the Bitcoin logo on one side and the holographic seal on the other.
25 BTC Gold-Plated Coins: Aimed at more significant investors, these coins were gold-plated and carried a higher Bitcoin value.
5 BTC Nickel Coins: A rarer denomination, these coins were made of nickel brass and were produced for just one year, making them particularly sought after by collectors.
Each coin’s hologram displayed the Bitcoin address associated with the coin’s value, allowing holders to verify the balance without revealing the private key. To access the digital funds, one would peel off the hologram, exposing the private key and rendering the physical Bitcoin coin’s digital value spent.
Regulatory Challenges and Cessation
The innovative nature of Casascius coins soon attracted regulatory attention. In 2013, the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) raised concerns regarding the minting and distribution of physical Bitcoin currency linked to digital assets. Specifically, they questioned whether Caldwell’s activities might be subject to money transmission regulations. Facing potential legal challenges, Caldwell ceased production of loaded Casascius coins in November 2013.

Collectibility and Market Value
Today, Casascius coins are highly prized collectibles within both numismatic and cryptocurrency communities. Their value is influenced by several factors:
Bitcoin Content: The inherent Bitcoin value of the coin plays a significant role. For instance, a 25 BTC coin’s worth is directly tied to the current Bitcoin market price.
Redeemed vs. Unredeemed: Coins with intact holograms (unredeemed) are generally more valuable than those with exposed private keys (redeemed), as the former still contain their digital Bitcoin.
Condition and Rarity: Coins in mint condition, especially those from limited runs or unique denominations, command higher premiums.
For example, as of recent auctions, a 2011 25 BTC gold-plated Casascius coin in pristine condition fetched significant sums, reflecting both its digital and collectible worth.
Legacy and Impact
Casascius coins hold a unique place in the history of Bitcoin:
Tangible Connection: They provided a physical form to an otherwise intangible asset, aiding in broader public understanding and acceptance of cryptocurrencies.
Educational Tool: These coins served as educational instruments, helping individuals grasp the concept of digital wallets, private keys, and the importance of security in cryptocurrency transactions.
Collector’s Item: Over time, they’ve become coveted artifacts, symbolizing the early days of Bitcoin and the community’s innovative spirit.
Conclusion on Physical Bitcoin
Mike Caldwell’s Casascius coins represent a fascinating intersection of the digital and physical worlds. They not only offered a novel way to engage with Bitcoin but also highlighted the challenges and opportunities at the dawn of the cryptocurrency era. Today, these coins stand as testament to Bitcoin’s journey from a niche digital experiment to a mainstream financial phenomenon.
Stay tuned to The BIT Journal and keep an eye on Crypto’s updates.
FAQs
What is a Casascius coin?
A physical Bitcoin created by Mike Caldwell, containing an embedded private key corresponding to a specific amount of digital Bitcoin
Are Casascius coins still in production?
No, production ceased in 2013 due to regulatory concerns.
How can I verify the value of a Casascius coin?
By checking the Bitcoin address displayed on the coin’s hologram using a blockchain explorer.
Do Casascius coins have value beyond their Bitcoin content?
Yes, they are considered collectibles and often have numismatic value exceeding their digital Bitcoin worth.
Glossary
Bitcoin (BTC): A decentralized digital currency without a central bank or single administrator.
Private Key: A secret code that allows the holder to access and manage their cryptocurrency funds.
Holographic Seal: A tamper-evident sticker used on Casascius coins to protect the embedded private key.
Redeemed Coin: A Casascius coin whose private key has been exposed and its digital Bitcoin accessed.
Unredeemed Coin: A Casascius coin with an intact hologram, indicating its digital Bitcoin remains untouched.